
Top Customer Support Models in 2025 You Must Know
Elevate Your Customer Support in 2025
Want better customer support that boosts sales and satisfaction? This listicle explores seven key customer support models to help you choose the right strategy. Learn how each model works, who it benefits, and how to implement it for maximum impact. Discover the best approach for your business, whether you need 24/7 availability, personalized interactions, or scalable solutions. Choosing the right customer support model is critical for efficiency and growth. Let's explore these options:
1. Tiered Support Model
The Tiered Support Model is a popular customer support model that organizes agents into different levels based on their expertise and the complexity of the issues they handle. This model typically consists of three or four tiers, ranging from Level 1 (front-line support for basic issues) to Level 3 or 4 (expert technical support for complex problems). Each tier has a specific area of focus, with clear escalation paths defined for moving issues up the chain when necessary. This structured approach allows businesses to efficiently allocate resources and ensure that customer issues are resolved by the most appropriate agent. This model deserves a place on this list due to its widespread adoption and proven effectiveness in managing customer support operations for businesses of all sizes. Its scalability, cost-effectiveness, and focus on specialized expertise make it a valuable framework for delivering quality customer service.
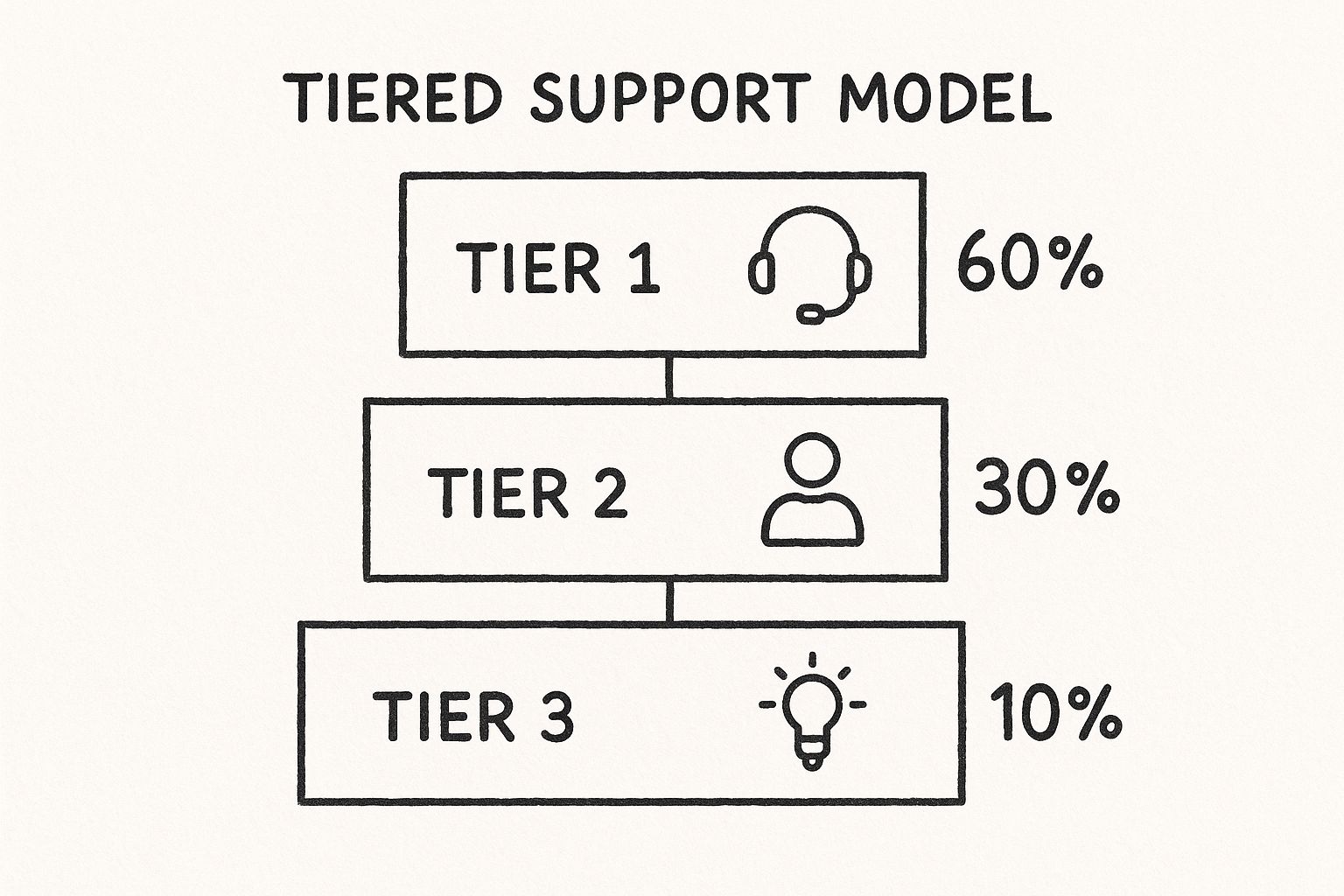
The infographic visualizes the hierarchical structure of a tiered support model. It demonstrates the flow of a customer issue through the different support levels, starting with Tier 1 (front-line support) which handles the most common and straightforward problems. As complexity increases, issues are escalated to Tier 2 (technical support), and potentially further up to Tier 3 (engineering/product specialists) for the most complex and specialized situations.
The Tiered Support Model offers several key features: multiple support levels, clear escalation paths, specialization at higher tiers, cost-efficient resource allocation, and structured knowledge management. This allows for streamlined handling of simple, repetitive issues at the lower tiers, freeing up specialized agents at higher tiers to focus on complex problems. The clear progression path from Tier 1 to higher tiers also offers a structured career path for support staff. Learn more about Tiered Support Model (https://chatisto.com/blog/scaling-customer-support). This structure also promotes scalable support for growing businesses.
Pros:
- Efficient handling of simple, repetitive issues at lower tiers
- Technical specialists can focus on complex problems
- Clear career progression path for support staff
- Scalable for organizations of various sizes
- Cost-effective resource allocation
Cons:
- Multiple handoffs can frustrate customers
- Knowledge silos may develop between tiers
- Potential for longer resolution times due to escalations
- May create artificial barriers between support levels
- Can lead to a "passing the buck" mentality
Examples of Successful Implementation:
Several major companies successfully utilize tiered support models, including Apple's technical support structure with AppleCare tiers, Microsoft's enterprise support services, and Amazon Web Services (AWS) Support Plans. These companies demonstrate the scalability and effectiveness of this model across diverse industries.
When and Why to Use a Tiered Support Model:
This approach is particularly beneficial for growing tech companies (SaaS/B2B), e-commerce platforms wanting 24/7 shopper assistance, and large enterprises in need of custom integrations and dedicated support. It is also an excellent model for small businesses looking for cost-effective ways to provide comprehensive customer support.
Tips for Implementation:
- Implement clear escalation criteria and procedures.
- Create comprehensive knowledge bases accessible across all tiers.
- Develop regular cross-training programs between tiers to mitigate knowledge silos.
- Use customer satisfaction metrics to identify and address escalation issues.
- Consider allowing tier-skipping for particularly complex issues to improve resolution times.
2. Follow-the-Sun Support Model
The Follow-the-Sun Support Model is a powerful approach to customer support that ensures 24/7 availability without burning out your team. It works by strategically distributing support teams across different time zones. As one team finishes their day, they hand off ongoing customer issues to the next team starting their workday in the next time zone. This creates a continuous loop of support, like the sun's journey across the sky, hence the name. This model is a key player among various customer support models because of its ability to provide uninterrupted service.
How it Works: Imagine your primary support team is located in London. As their workday ends, they pass unresolved issues to a team in New York. When the New York team finishes, they hand off to a team in California. Finally, as the California team's day ends, the cycle completes with issues being handed back to the London team, who are now starting their day. This continuous cycle ensures no customer query goes unanswered, regardless of the time.
Features and Benefits:
- 24/7 Availability: The most significant advantage is uninterrupted support coverage. Customers never encounter "closed" messages or delayed responses.
- No Overnight Shifts: Employees maintain regular working hours, promoting a healthy work-life balance and reducing burnout.
- Faster Resolution Times: Issues can be addressed promptly, minimizing customer wait times and improving satisfaction.
- Global Reach: Ideal for businesses with an international customer base, offering support in multiple languages and catering to diverse cultural nuances.
- Knowledge Sharing and Collaboration: Distributed teams foster a global perspective and facilitate the sharing of best practices and solutions.
Pros and Cons:
Pros:
- Continuous support without requiring night shifts
- Faster resolution times for complex issues
- Better work-life balance for support staff
- Global coverage for multinational businesses
- Ability to support customers in multiple languages
Cons:
- Complex to implement and manage, requiring significant investment in multiple locations and infrastructure.
- Potential for communication issues during handoffs if processes aren't well-defined.
- Cultural and language differences may impact consistency if not carefully addressed.
- Higher overhead costs compared to centralized models.
When and Why to Use This Approach:
This customer support model is particularly beneficial for:
- Growing tech companies (SaaS/B2B): Scaling support operations to match rapid growth and providing round-the-clock service to a global client base.
- E-commerce platforms: Offering 24/7 shopper assistance to maximize sales and customer satisfaction in a competitive online market.
- Large enterprises: Managing high volumes of support requests from a geographically diverse customer base.
- Global businesses: Serving customers across multiple time zones with consistent and timely support.
Examples of Successful Implementation:
Several leading companies leverage the Follow-the-Sun model, including:
- IBM's Global Support Centers
- Oracle's Global Customer Support
- Microsoft's Global Technical Support Services
- Accenture's global support operations
- Cisco Systems' global technical assistance centers
Tips for Implementing a Follow-the-Sun Model:
- Robust Case Management System: Implement a system that facilitates seamless handoffs and ensures all information is readily available to each team.
- Standardized Processes: Develop clear and consistent processes for handling customer queries across all locations.
- Regular Communication: Schedule regular virtual meetings between regional teams to foster collaboration and address any challenges.
- Detailed Handoff Protocols: Create detailed protocols to ensure smooth transitions between teams and prevent information loss.
- Cultural Training: Invest in cultural sensitivity training to bridge regional differences and improve communication effectiveness.
This model deserves its place on this list because, despite its complexities, it offers unparalleled benefits for businesses seeking to provide truly global, 24/7 customer support. By thoughtfully implementing the tips outlined above, businesses can mitigate the challenges and reap the rewards of this powerful customer support model.
3. Swarming Support Model
The Swarming Support Model represents a significant departure from traditional tiered customer support models. Instead of routing inquiries through escalating levels of expertise, swarming brings together a cross-functional team of specialists to collaboratively tackle complex customer issues in real-time. Think of it as a "swarm" of experts converging on a problem to quickly and efficiently find a solution. This eliminates the frustrating back-and-forth and extended wait times often associated with traditional support systems. The focus is on collaboration, knowledge sharing, and direct customer interaction with the right people at the right time, ultimately leading to faster resolutions and happier customers.

This customer support model is particularly effective for handling complex issues that require a diverse range of expertise. Imagine a technical problem that involves software, hardware, and networking components. Instead of bouncing the customer between different support tiers, a swarm team comprised of specialists from each area can work together simultaneously, diagnosing and resolving the problem much faster. This approach not only reduces resolution time but also enhances knowledge sharing within the organization. Team members learn from each other during the swarming process, leading to a more skilled and versatile support team overall.
Features of the Swarming Support Model:
- Cross-functional teams: Specialists from different areas collaborate on complex issues.
- Real-time problem solving: Issues are addressed immediately, without formal escalations.
- Dynamic team formation: Teams are assembled based on the specific requirements of each issue.
- Direct customer interaction: Customers communicate directly with the experts best equipped to solve their problems.
- Collaborative knowledge building: The swarming process facilitates knowledge sharing across specialties.
Pros:
- Faster resolution of complex issues
- Reduced customer frustration from multiple handoffs
- Enhanced knowledge sharing across the organization
- Higher first-contact resolution rates
- Improved employee satisfaction through collaborative work
Cons:
- Resource-intensive for simpler issues
- Requires high level of coordination and communication
- May be challenging to scale efficiently
- Difficult to implement in organizations with rigid hierarchies
- Success depends heavily on a collaborative culture
Examples of Successful Implementation:
- Atlassian's collaborative support approach
- Cisco's High-Touch Technical Support
- Red Hat's collaborative support model
- Zappos' team-based customer service
- GitHub's engineering-integrated support
Tips for Implementation:
- Start small: Begin with pilot programs for specific complex issue types.
- Invest in collaboration tools: Implement robust collaboration platforms for seamless communication.
- Define clear protocols: Develop clear protocols for when to initiate swarms.
- Capture knowledge: Create mechanisms for documenting and sharing knowledge gained during swarms.
- Measure collaboration: Establish metrics that prioritize collaborative efforts over individual performance.
When and Why to Use the Swarming Support Model:
This model is best suited for organizations dealing with technically complex products or services, where customer issues often require a multi-faceted approach. Growing tech companies (SaaS/B2B), e-commerce platforms facing complex technical challenges, and large enterprises needing rapid solutions for critical issues can benefit significantly. While it might not be the most efficient model for handling simple inquiries, the Swarming Support Model offers a powerful way to tackle complex problems, improve customer satisfaction, and foster a more collaborative and knowledgeable support organization. It deserves a place on this list because it represents a truly innovative and effective approach to customer support, particularly for businesses operating in complex environments. It empowers support teams to move beyond traditional, tiered systems and embrace a dynamic and collaborative approach to problem-solving. This, in turn, leads to faster resolution times, increased customer satisfaction, and a more knowledgeable and engaged workforce. The swarming model is especially relevant in today's fast-paced business world where customer expectations are higher than ever.
4. Self-Service Support Model
The Self-Service Support Model is a key player among various customer support models, empowering customers to resolve their issues independently. It achieves this by providing a comprehensive suite of resources like knowledge bases, FAQs, community forums, chatbots, and other automated tools. This model prioritizes creating easily accessible information repositories, allowing customers to find answers without needing to contact a support agent directly. When implemented effectively, a robust self-service strategy reduces support costs and simultaneously improves customer satisfaction by offering immediate solutions.
How it Works:
The core of self-service support revolves around anticipating customer questions and proactively providing the answers. This involves:
- Creating a Comprehensive Knowledge Base: This is the central hub of information, containing articles, tutorials, and FAQs covering a wide range of topics related to your product or service.
- Implementing Smart Search Functionality: Users should be able to easily find what they're looking for using natural language processing and robust search algorithms.
- Leveraging Automation: Chatbots and virtual assistants can guide customers through troubleshooting steps, answer common questions, and even escalate complex issues to human agents when necessary.
- Fostering Community: Forums and peer-to-peer support platforms allow customers to learn from each other and share solutions.
- Providing Visual Guidance: Video tutorials and interactive guides can be particularly helpful for explaining complex processes.
Examples of Successful Implementation:
- Microsoft: Their extensive support documentation and community forums provide answers to a vast array of technical questions, allowing users to troubleshoot issues independently.
- Amazon: Their streamlined self-service return and refund process empowers customers to manage their orders without needing to contact customer support.
- Spotify: Their help center and troubleshooting guides address common listening issues and account management questions, ensuring a smooth user experience.
- Apple: The Apple Support App and knowledge base offer comprehensive resources for troubleshooting device problems and accessing user manuals.
- Zendesk: Zendesk offers powerful self-service portal options for businesses to build customized knowledge bases and community forums.
Pros and Cons:
Pros:
- 24/7 Availability: Resources are accessible anytime, anywhere.
- Cost Savings: Reduces the need for a large support team, leading to significant cost reductions.
- Scalability: Easily adapts to a growing customer base without requiring proportional increases in support staff.
- Customer Preference: Many customers prefer self-service for quick answers to simple questions.
- Reduced Agent Workload: Frees up agents to handle more complex and demanding issues.
- Consistency: Ensures all customers receive the same accurate information.
Cons:
- Limited Scope: Not suitable for complex or unique customer issues.
- Initial Investment: Requires significant effort in content creation and ongoing maintenance.
- Potential for Frustration: Outdated or poorly organized content can lead to negative customer experiences.
- Impersonal: May lack the personal touch of human interaction.
- Content Dependent: Effectiveness relies heavily on high-quality, easily searchable content.
Actionable Tips:
- Regular Audits: Regularly review and update your knowledge base to ensure accuracy and relevance.
- Analytics Integration: Track usage data to identify content gaps and understand customer search behavior.
- Escalation Paths: Provide clear pathways for customers to contact human support when self-service isn't sufficient.
- Feedback Integration: Use customer feedback to improve self-service resources and address pain points.
- Mobile Optimization: Ensure your self-service resources are accessible and user-friendly on mobile devices.
- Search Analytics: Monitor search queries to understand what customers are looking for and optimize content accordingly.
When and Why to Use Self-Service:
This model is particularly beneficial for:
- Handling Frequently Asked Questions: Address common inquiries proactively to reduce support ticket volume.
- Providing Basic Troubleshooting: Guide users through simple fixes for common problems.
- Empowering Customers: Give customers the tools to resolve issues on their own, fostering independence and satisfaction.
- Scaling Support Operations: Provide efficient support to a large customer base without significant staffing increases.
Why it Deserves its Place in the List:
The Self-Service Support Model is an essential component of a modern customer support strategy. It offers a cost-effective and efficient way to provide 24/7 assistance, empower customers, and free up support agents to focus on more complex issues. In today's digital landscape, where customers expect instant answers, a well-designed self-service portal is no longer a luxury but a necessity.
5. Proactive Support Model
The Proactive Support Model represents a significant shift in customer support philosophy, moving from reactive problem-solving to anticipating and addressing potential issues before they impact the customer. Instead of waiting for a customer to report a problem, this model uses data analysis, monitoring tools, and an understanding of customer behavior patterns to identify and resolve issues proactively. This focus on prevention rather than remediation leads to a significantly improved customer experience while simultaneously reducing the overall volume of support requests. This makes it a powerful model for businesses of all sizes, from small startups to large enterprises.
This approach works by leveraging several key features:
- Predictive Analytics: Analyzing historical data to forecast potential issues and trends.
- Automated Monitoring Systems: Real-time monitoring of systems and applications to detect anomalies and potential problems early on.
- Proactive Customer Outreach: Contacting customers about known issues or upcoming maintenance before they experience any disruption.
- Regular Health Checks and Preventative Maintenance: Performing routine checks and maintenance to prevent potential problems from occurring.
- Personalized Recommendations: Offering tailored advice and solutions based on individual customer usage patterns.
- Preemptive Notifications: Informing customers about system changes, planned maintenance, or potential service interruptions.
Several successful companies are already utilizing proactive support:
- Amazon Web Services (AWS) Health Dashboard: Provides real-time information on the health of AWS services, allowing users to anticipate and prepare for potential disruptions.
- Microsoft's predictive maintenance for Azure services: Uses machine learning to predict and prevent hardware failures in Azure data centers.
- Salesforce's Trust site for service status: Offers transparent updates on the status of Salesforce services, enabling customers to stay informed about potential issues.
- Tesla's remote diagnostics and proactive maintenance alerts: Tesla vehicles can remotely diagnose potential problems and notify owners about necessary maintenance.
- Adobe's proactive security patches and updates: Adobe proactively releases security patches and updates to protect users from potential vulnerabilities.
Why choose a Proactive Support Model? Its benefits are substantial:
- Reduces Support Ticket Volume: By preventing issues, you'll see fewer customers needing to contact support.
- Improves Customer Satisfaction and Loyalty: Proactive support demonstrates a commitment to customer success, fostering trust and loyalty.
- Prevents Escalation: Minor issues are addressed before they become major problems, saving time and resources.
- Creates Positive Interactions: Proactive outreach provides opportunities for positive engagement with customers.
- Identifies Systemic Issues: Analyzing patterns of potential problems can reveal underlying systemic issues affecting multiple customers.
However, there are some potential drawbacks to consider:
- Requires Sophisticated Data Analytics: Implementing proactive support requires robust data analytics capabilities.
- Higher Initial Investment: Investing in monitoring and predictive tools can be costly upfront.
- Risk of False Positives: Inaccurate predictions can lead to unnecessary work and potentially annoy customers.
- Potential for Intrusiveness: Proactive outreach can be perceived as intrusive if not handled carefully.
- Difficult ROI Measurement: Measuring the return on investment for prevented issues can be challenging.
Tips for Implementing Proactive Support:
- Start Small: Begin by monitoring critical systems and customer touchpoints.
- Develop Clear Protocols: Establish clear guidelines for when and how to proactively contact customers.
- Respect Customer Privacy: Balance proactive outreach with respect for customer privacy and preferences.
- Use Templates: Create templates for common proactive communications to ensure consistency and efficiency.
- Measure and Iterate: Track both prevented issues and customer responses to proactive outreach, and continuously refine your approach based on the data.
- Integrate Feedback Loops: Gather customer feedback to improve the accuracy of your predictive capabilities.
This proactive approach is particularly popular with SaaS and subscription-based businesses, those employing Customer Success methodologies, enterprise technology providers, and companies specializing in predictive analytics. If your business fits into one of these categories, or if you’re simply looking for ways to improve customer satisfaction and reduce support costs, the Proactive Support Model deserves serious consideration. Learn more about Proactive Support Model It can be a powerful tool for building stronger customer relationships and ensuring long-term success. This approach helps differentiate your customer support, moving it from a cost center to a value driver for your business. It's a critical element of the evolving landscape of customer support models.
6. Omnichannel Support Model
The Omnichannel Support Model represents the gold standard in modern customer service. Unlike other customer support models, it's designed to provide a completely seamless and integrated experience, regardless of how a customer chooses to interact with your business. This approach recognizes that customers don't think in terms of individual channels like "phone" or "email"—they simply want their issue resolved efficiently and conveniently. In the crowded landscape of customer support models, omnichannel stands out by prioritizing a unified and personalized customer journey. This model deserves its place on this list because it represents the future of customer interaction, focusing on building strong relationships and enhancing customer loyalty.
Instead of treating each communication channel (phone, email, live chat, social media, messaging apps, even in-person interactions) as separate silos, omnichannel support weaves them together into a unified whole. Imagine a customer starting a conversation with a chatbot on your website, then seamlessly switching to email for more complex questions, and finally resolving the issue over the phone without having to repeat any information. That's the power of omnichannel.
How it Works:
The core of omnichannel support is a centralized database that tracks all customer interactions across all channels. This provides agents with a 360-degree view of each customer, including their past purchases, support requests, and preferences. This unified customer view empowers agents to provide personalized and efficient support, regardless of the communication channel. The system remembers the context of the conversation, so customers don't have to repeat themselves as they move between channels.
Features and Benefits:
- Unified customer view: Access a complete customer history across all touchpoints.
- Seamless channel transitions: Customers can effortlessly switch between channels.
- Consistent experience: Maintain a consistent brand voice and service quality across platforms.
- Centralized interaction history: Track all customer interactions in a single location.
- Channel-appropriate responses: Tailor responses to the specific channel while maintaining consistent information.
- Integrated customer journey mapping: Identify and eliminate friction points across the entire customer journey.
Pros:
- Improved customer satisfaction: Convenience and consistency lead to happier customers.
- Higher resolution rates: Access to complete interaction history enables faster and more effective problem-solving.
- Reduced customer effort: No more repeating information or navigating complex support processes.
- Better data collection: Gain valuable insights into customer behavior and preferences.
- Meet customers where they are: Engage with customers on their preferred channels.
- More efficient agent utilization: Agents can handle multiple channels concurrently, improving productivity.
Cons:
- Complex and costly implementation: Integrating systems and data requires significant investment.
- Maintaining consistent quality: Ensuring consistent service quality across all channels can be challenging.
- Agent training: Agents need training to handle multiple communication methods effectively.
- Technology dependencies: Seamless integration relies on robust technology infrastructure.
Examples of Successful Implementation:
- Disney's MyMagic+: Seamlessly integrates digital and physical touchpoints for a magical customer experience.
- Bank of America: Provides a unified banking experience across mobile, web, ATM, and in-person interactions.
- Starbucks: Integrates mobile ordering with the in-store experience for a streamlined coffee run.
- Sephora: Connects online and in-store customer profiles for a personalized beauty experience.
- Zappos: Known for its exceptional customer service across multiple channels.
Actionable Tips for Implementation:
- Start small: Begin by integrating your most frequently used channels.
- Prioritize data unification: Focus on unifying your customer data before adding new channels.
- Train your team: Equip your support staff with the skills to handle multiple communication methods.
- Map the customer journey: Identify and address any friction points in the cross-channel experience.
- Consistent metrics: Track the same key performance indicators (KPIs) across all channels.
- Consistent brand voice: Maintain a unified brand voice and messaging across all touchpoints.
When and Why to Use Omnichannel Support:
Omnichannel support is ideal for businesses committed to providing exceptional customer experiences and building long-term customer loyalty. It’s particularly beneficial for:
- Growing tech companies (SaaS/B2B): Scaling support and sales efforts efficiently.
- E-commerce platforms: Offering 24/7 shopper assistance and personalized recommendations.
- Large enterprises: Managing complex customer interactions across multiple departments and channels.
- Customer support teams: Boosting conversions, improving efficiency, and increasing customer satisfaction.
Learn more about Omnichannel Support Model This link offers valuable insights into implementing live chat, a crucial component of an effective omnichannel strategy. Remember, choosing the right customer support model is crucial for business success. Omnichannel, while demanding, offers the greatest potential for delivering truly exceptional customer experiences.
7. Community-Based Support
Community-based support models leverage the collective knowledge and experience of your customer base to provide assistance and solve problems. This model fosters a sense of ownership and shared responsibility among users, often leading to quicker resolution times and increased customer satisfaction. It can be a powerful addition to your existing customer support models, especially for growing businesses.
This approach works by creating a platform – typically a forum, online community, or social media group – where customers can interact with each other, ask questions, share tips, and troubleshoot issues. Often, experienced users will answer questions and provide solutions before a support agent needs to intervene. This not only reduces the workload on your support team but also creates a valuable resource of user-generated content and solutions.
Examples of Successful Implementation:
- Software companies: Many software companies use forums to allow users to share tips, troubleshoot bugs, and request new features. For example, companies like Adobe and Autodesk have thriving community forums.
- Gaming companies: Online gaming communities often rely on player-to-player support for in-game issues and technical troubleshooting.
- E-commerce platforms: Some e-commerce businesses create Facebook groups where customers can ask questions about products, share reviews, and get help from other users.
Actionable Tips for Readers:
- Choose the right platform: Select a platform that aligns with your target audience and business needs. Consider factors like ease of use, moderation capabilities, and integration with existing tools.
- Seed the community: Initially, you might need to actively participate in the community to encourage engagement and answer questions.
- Recognize and reward active members: Highlighting valuable contributions can motivate users to continue participating and helping others.
- Establish clear guidelines: Set community guidelines to maintain a positive and productive environment.
- Integrate with other support channels: Make it easy for users to escalate issues to your support team if they can't find a solution within the community.
When and Why to Use This Approach:
Community-based support is particularly beneficial for:
- Scalability: It allows you to handle a growing volume of support requests without proportionally increasing your support team size.
- Cost-effectiveness: It can significantly reduce support costs by leveraging the power of the community.
- Building customer loyalty: It fosters a sense of community and belonging among your customers.
- Gathering product feedback: Community forums can be a valuable source of insights into customer needs and preferences.
Pros:
- Reduced support costs
- Increased customer satisfaction
- Scalable solution
- Valuable source of user-generated content
Cons:
- Requires ongoing moderation
- May not be suitable for all types of businesses
- Can be challenging to build a thriving community
- Requires clear guidelines and community management
This approach deserves its place in the list of customer support models because it offers a unique blend of cost-effectiveness, scalability, and community building. By empowering customers to help each other, businesses can create a more sustainable and engaging support experience while also reducing their operational costs. This makes community-based support an attractive option for businesses of all sizes, particularly those experiencing rapid growth or operating in niche markets with highly engaged user bases. It's an excellent strategy for enhancing customer satisfaction and building a loyal customer base.
Customer Support Models Comparison
| Model | Implementation Complexity 🔄 | Resource Requirements ⚡ | Expected Outcomes 📊 | Ideal Use Cases 💡 | Key Advantages ⭐ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tiered Support Model | Moderate - requires tier design and escalation paths | Moderate - multiple specialized teams | Efficient issue resolution, cost-effective handling | Organizations needing structured escalation and scalability | Clear escalation workflow, cost-effective, scalable |
| Follow-the-Sun Support Model | High - global coordination, time zone management | High - multiple international support centers | 24/7 continuous support, faster resolution | Global businesses with customers in varied time zones | Round-the-clock support, better staff work-life balance |
| Swarming Support Model | High - requires culture shift and coordination tools | High - cross-functional collaboration needed | Faster complex issue resolution, improved satisfaction | Complex problems needing expert collaboration | Eliminates handoffs, enhances knowledge sharing |
| Self-Service Support Model | Low to Moderate - requires solid content creation | Low to Moderate - investment in knowledge bases and automation | Reduced agent workload, 24/7 issue resolution | High-volume, routine issues suitable for automation | Cost savings, accessible anytime, scalable |
| Proactive Support Model | High - data analytics and monitoring tools required | High - investment in analytics and monitoring | Reduced ticket volume, improved customer loyalty | Businesses aiming to prevent issues before they occur | Prevents problems, improves experience and loyalty |
| Omnichannel Support Model | High - integrates multiple systems and channels | High - technology and training for multiple channels | Seamless customer experience across channels | Brands wanting consistent experience across platforms | Consistent, unified experience, higher resolution rate |
Choosing the Right Model for Your Business
Finding the perfect fit among the various customer support models—from tiered and follow-the-sun to swarming and self-service—is crucial for business success. The most effective model will depend on factors like your company size, industry, customer expectations, and budget. This article explored several key customer support models, highlighting their strengths and ideal use cases. You might find that a single model perfectly addresses your needs, or perhaps a hybrid approach combining elements of several models is the optimal solution. For instance, blending tiered support with robust self-service resources and proactive outreach can create a comprehensive and powerful support strategy.
Key takeaways include understanding the core principles of each model and recognizing how they can be adapted to fit specific business requirements. Mastering these concepts empowers you to create a customer support experience that fosters satisfaction, builds loyalty, and ultimately fuels growth. Quality assurance is crucial for evaluating and enhancing the effectiveness of various customer support models. For a deeper understanding of call center quality assurance and its impact, check out this helpful resource: call center quality assurance.
By optimizing your customer support strategy, you can streamline operations, reduce costs, and create a positive brand image. Remember, customer support isn't just about resolving issues; it's about building relationships and fostering long-term customer value.
Ready to take your customer support to the next level? Explore how Chatisto, an AI-powered customer support solution, can enhance your chosen support model by automating routine tasks and enabling smart handoff capabilities for seamless customer interactions. Discover how Chatisto can help you optimize efficiency and create exceptional support experiences.